Welcome to this week’s edition of The Weekly Climate 🎉
References: [1], [2], [3], [4] and [5].
This was a pretty crazy week. I mean just the two main “attractions”: Greenpeace’s undercover operation that revealed a lot about how the fossil fuel industry works with politicians just as the ocean caught on fire and a heat dome killed more than 400 people in North America, along with wildfires and heat records beaten many places.
‼️News you can’t miss
Here’s one important scary/bad (🙀), good (😻), interesting (😼) and fossil (💩) news item.
🙀 EU will be ripped apart by climate change according to Politico study.
😻 12% drop in emissions for new cars in the EU in 2020
😼 Advances in climate science makes it easier to sue the companies and countries causing the climate crisis.
💩 Two Exxon lobbyists caught spilling the beans in everything from shadow groups to how to counter climate action.
👩⚕️ Status: Climate & Science
Let’s look at how we’re doing this week!
[#antarctica] — A new report confirms the highest so far measured temperature in Antarctica from February last year. A whopping 18.3C was confirmed by the UN.
[#heatdome] — Here’s a good explanation of how the so called heat dome over western US formed last week and as climate scientists argue nowhere is really safe from these. Heat extremes are predicted and totally expected by all climate scientists.
[#lytton] — Just before Lytton, BC burned to the ground it registered the highest temperature ever recorded in Canada: 49.6C … 3 days in a row.
[#lawsuits] — A new report makes it clear that advanced in climate science is likely to spur a whole new wave of lawsuits against various polluters because it is now possible to attribute concrete damages to the companies emissions. Anybody who knows a lawyer, let’s do this!
📰 The 7 Grand Challenges
⚡️Decarbonize Electricity
Clean electricity is the one do-or-die challenge we must solve.
[#solarfarmers] — I’ve posted a few articles about how agriculture and solar can interact in good ways but this article looks at an interesting related trend in the UK in which land owners increasingly swaps out crops for solar power. The reason for the surge is likely that a utility scrapped the upfront cost of connecting a utility scale solar power plant to the grid.
[#coal] — In attempt to beef up it’s climate credentials prior to COP26, the UK has announced that it will end all coal power in the country by 2024.
[#hydro] — A new report by the IEA hails one of the often forgotten renewable energy sources: Hydro power. Hydro is expected to grow by 17% in the next decade led by China, India, Turkey and Ethiopia. However, it does appear that hydropower growth is slowing down, therefore IEA calls for more investments and government support.
🏘 Reduce impact of urban and rural areas
Lowering the impact of urban and rural areas.
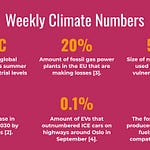
[#cars] — As I’ve shared in the past newsletters EVs have had a great year in 2020 especially in the EU. And with that comes obviously a drop in average emissions for new cars sold in region. The average emissions of a new car fell by 12% to 107.8 gCO2 / km.
[#heatpump] — In case you didn’t know an electric heat pump is actually also a cold pump, i.e. it can run in two ways. So this article dives into how heat pumps is a great climate solution as well as how they can help during heat waves.
[#ev] — A new study has found that implementing more intelligent charging of EVs could reduce the emissions from charging them by up to 14%. More intelligent charging could mean for instance taking advantage of solar and batteries in people’s homes or only charging when there’s a sufficiently high amount of renewables active on the grid.
🛁 Clean non-electrifiable activities
Some activities we do today can’t be electrified, these must be cleaned some other way.
[#plastic] — A new report has been published that calls for a global treaty to end the production of so called ‘virgin plastic’ by 2040. Since 1950s we have produced 8 billion tonnes of plastic and much of that ends up in the oceans and landfills. Some of the big posts on the plastic budget is: Packaging materials with 47% of all plastic, 14% from textiles and 6% from transport.
[#cement] — Here’s an interview with the founders of Alcemy, which have developed AI-based software that can increase the precision and accuracy of cement production hereby lowering the overall production of cement.
🌳 Protect and grow nature
Nature is our ally, we must protect it and help it help us.
[#heatwaves] — There’s one solution to adapt to the increasing number and intensity of heatwaves which also happens to be a great carbon removal solution, and that is trees. Researchers have found that trees can lover the temperature of it’s surroundings by around 6C. The problem though is that trees are not having an easy time in cities. This article looks at that problem.
[#offsets] — Here’s a couple of examples of flaws offsets in which an offsetting program promised forest protection and got rewarded multiple millions $ for it, only to have Global Forest Watch discover that forest cover actually decreased in the period they were paid for. And it’s not the only place where this is happening. Another report has revealed that carbon offsets offered in Colombia has not only been used by companies to dodge taxes but also overstate their impact on forest protection.
🍽 Optimize food
Without the lower impact of food or drink the hero doesn’t work (modified old danish proverb).
[#plastic] — Researchers have found an enzyme in the stomach of cows that can break down common plastics. An immediate question is presents itself: Why? Apparently much of cows food contain a kind of shell with similar structures as plastic hence this is why the researchers think the cows have evolved to have that enzyme. The image of cows munching down plastic though is a pretty horrible one.
⚖️ Climate Justice
Without justice there’s no future.
[#lawsuits] — Here’s a slide-based overview of the rise in fossil fuel based lawsuits. In the last decade more than 700 lawsuits have been filed against the fossil fuel industry. Right from cities suing because they’ve been forced to build a sea wall to more widely scoped public nuissance lawsuits because the impact of fossil fuels have made areas less livable. The slide-based overview is followed up by a more in-depth article on the matter.
📦 Other / catch-all
All the other stuff that I couldn’t fit into any of the other categories, than the other category.
[#wildfire] — Here’s an inspiring video produced by the US Department of Natural Resources about how wildfires are affecting big parts of the US and how the people has recovered from these traumatic and lifechanging experiences.
[#climatetech] — Two very interesting discussions on the Interchange podcast. The first one titled “🎧Where are the gaps in climate tech” looks at the state of climate tech, where the gaps are and discusses how big the impact ultimately will be. The other one is titled “🎧The New ‘Valleys of Death’ in climate investing” looks at why climate tech companies dies starting off with the beginning of the cleantech crisis in 2011 and back to the future.
⭐️Special Topics
🎩 Global and local policy
We have a special interest in covering the major global and local policies regarding climate, whether good or bad.
[#ranking] — Australia ranks worst on a list for climate action among all 192 UN member states says a new report. Australia is followed by Brunei, Qatar and Norway. Finland, Denmark and Sweden are 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
🛡 Adaptation
Adapting our civilization to the coming climate crisis is vital. Here we cover various ways that is happening (or isn’t).
[#EU] — Politico did a survey of a 100 scientific papers looking at what will happen to the EU in the case of 1.5C and 2C temperature increases. And their findings are pretty scary. Both ends of the continent (north and south) will struggle with various problems. From fires and floods up north (even for the low temperature scenarios) and down south it will be droughts, heat and agricultural decline. The report argues that these very different but very hard problems will tear Europe apart. It’s a long but very interesting read.
[#heat] — The extreme heat wave on the US West coast this past week has broken so many heat records (even worst case climate models) that it’s hard to count them all and it makes it clear that we need to build cities differently to handle all that excess heat. Here’s an interview with a climate researcher about how cities can adapt. As the heatwave was at it’s top he drove around Portland, Oregon and measured temperatures of buildings and found that they could vary by as much as 4.5C. These differences can be lifesaving as many thousands have died from the heatwaves this past week and still many left to be found.
⛽️ Major Carbon Emitters
We have a special interest in covering the moving of the major carbon emitters as these are the key roadblock to climate action.
[#exxon] — The biggest news item from last week was the sneaky sting operation that Greenpeace’s Unearthed ran on two key Exxon lobbyists. Posing as recruiters they got a senior Exxon lobbyist to spill the beans on all of Exxon’s strategies and tactics for killing all climate action policies through “shadow groups” and manipulation of key senators. There’s topics like how they’re publicly supporting a carbon tax, but only because they know it will never become a reality right to outright stating that they aggressively fought climate science. The link I posted above was to Heated’s walkthrough, but here’s the link to the original piece on Unearthed. Probably the most rage inducing of all of this is Exxon CEO Darren Woods response: “We were shocked by these interviews and stand by our commitments to working on finding solutions to climate change,” F- you Darren and thank you Greenpeace 🙏.
Part 2 in the Exxon sting by Greenpeace was released later in the week and it dealt with how Exxon lobbyists have worked on making sure that regulations to kill plastic is being stopped.
Here’s a profile of some of the climate scientists who worked at Exxon and who back then sounded the alarm in scientific peer reviewed journals about the harm that the fossil fuel industry’s products is causing to the planet.
Oh and the ocean caught fire last week from a pipeline malfunction. Look at this.
[#ipcc] — Another draft IPCC report has been leaked which indicate that climate scientists are using strong language in terms of blaming the fossil fuel industry for the many curbed attempts at any real climate action. The report blames think thanks, trade groups and other third party groups for influencing policy that has had a detrimental effect on the world’s ability to tackle the climate crisis so far.
[#coal] — A new report by Carbon Tracker, reveals that just five Asian countries (China, India, Indonesia, Japan and Vietnam) are responsible for 80% of the world’s planned new coal capacity. Those 80% will add more than 600 coal power plants and a total of 300GW of dirty coal capacity on to the grid. More than 50% of this capacity (187GW) will be built in China.
[#china] — Here’s a detailed look at China’s industry and how much it pollutes. Turns out (as expected) that it emits so much that it’s very clear that China must decarbonize it rapidly to hit it’s 50% target by 2030.
[#china] — China’s biggest bank has decided not to fund a 2.8GW coal plant scheduled to be built in Zimbabwe. Good news, yet I wonder where they’re going to find those 2.8GW…
That’s it for this week folks!
Remember if you’re feeling down, angry or sad from some of the news in this newsletter one cure is to act. And one way you can always act that also happens to be one of the most powerful things you can do is to talk about it. That also works if what you just read made you hopeful or happy btw.
If you enjoyed this newsletter don’t forget to share it with your friends, coworkers or other people you think could benefit from getting it. If you got directed here by a friend or another link on the Internet don’t forget to subscribe!
See you all next week 👋