[Nov 6-12'23] Governments still love fossils
Climate change responsible for Middle East drought, Amazon deforestation at 5 year low, how 120 cities can reduce transport emissions and new production gap report.
Welcome to this week’s edition of The Weekly Climate 🎉
References: [1], [2], [3], [4] and [5].
‼️News you can’t miss
Here’s one important scary/bad (🙀), good (😻), interesting (😼) and fossil (💩) news item.
🙀 Climate change responsible for severe drought through out the Middle East
😻 Amazon deforestation reaches 5 year low
😼 Detailed analysis of how 120 cities could reduce their transport emissions
💩 New Production Gap report is out and governments still love the fossils
👩⚕️ Status: Climate & Science
Let’s look at how we’re doing this week!
[#middleeast] — High temperatures caused by climate change are driving an ongoing drought in Syria, Iraq, and Iran. The drought has led to crop failures, water shortages, and food insecurity, affecting millions of people in the region. The study finds that climate change has made the drought more intense and more likely to occur. The severity of the drought is no longer rare due to climate change. Other factors such as conflict, water management, and land degradation have also contributed to the severe impacts of the drought.
[#stillhottest] — According to European climate scientists, 2023 is virtually certain to be the hottest year on record globally. October 2023 was the warmest October on record, following the hottest September and summer months. The analysis, based on computer modeling and billions of measurements, shows that global temperatures are currently 1.43 degrees Celsius above the preindustrial average. The United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP28, is set to begin at the end of the month, emphasizing the need for urgent climate action.
[#greenland] — Greenland's mountain glaciers and floating ice shelves are melting faster than before, according to two separate studies. Peripheral glaciers have retreated twice as fast between 2000 and 2021 compared to the previous century. The shrinking glaciers contribute disproportionately to sea level rise. Additionally, ice shelves have shrunk by more than 35% since 1978, with three already collapsing. The research highlights the rapid melting of glaciers and the vulnerability of ice shelves, emphasizing the impact of global climate change on Greenland's ice.
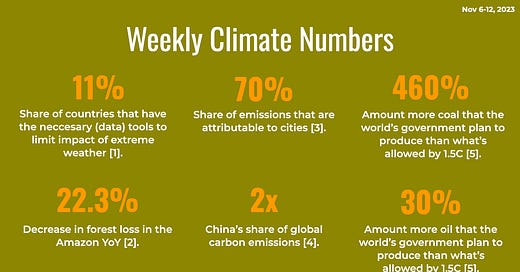
[#climatedata] — A report by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) reveals that only 11 percent of countries have the necessary tools to save lives in the face of extreme climate change impacts. Lack of access to climate data and early warning systems puts countries at a disadvantage, leading to more climate-related deaths. The report emphasizes the importance of investing in climate services to protect vulnerable populations from the consequences of global warming.
📰 The 7 Grand Challenges
⚡️Decarbonize Electricity
Clean electricity is the one do-or-die challenge we must solve.
[#fossilfuels] — A new United Nations report reveals that the world's top fossil fuel producing nations are planning to increase their output of oil, gas, and coal, far exceeding the climate targets set by the international community. Despite the majority of countries adopting net-zero pledges, their own plans and projections indicate that they are on track to extract more than twice the amount of fossil fuels by 2030 than would be consistent with limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius. This "production gap" between planned output and climate goals is a warning that the transition away from fossil fuels is off-course and jeopardizes humanity's future.
[#grid] — Electric school buses are being used as a solution to stabilize power grids and prevent blackouts. These buses, equipped with large batteries, can store excess renewable energy and release it back into the grid when needed. By harnessing the collective capacity of electric vehicles, rooftop solar panels, and home batteries, virtual power plants can be created to ensure a steady supply of electricity. While cost and infrastructure challenges remain, the potential benefits include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving public health, and creating a more reliable and sustainable energy system.
🏘 Reduce impact of urban and rural areas
Lowering the impact of urban and rural areas.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to The Weekly Climate to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.