[Mar 10-16'25] 🛰️ From Space to Soil
Climate Whiplash Hits Everything in Orbit
Welcome to this week's edition of The Weekly Climate 🎉
References: [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6]
‼️ News you can't miss
Here's one important scary/bad (🙀), good (😻), interesting (😼) and fossil (💩) news item.
🙀 [#Climate Language]: Trump's administration is systematically erasing climate-related language from federal websites and limiting scientific discussions, forcing researchers to find creative workarounds to continue their work.
😻 [#Renewable Growth]: Despite political headwinds, solar and wind energy have generated more electricity than coal for the first time in US history, marking a watershed moment in the energy transition.
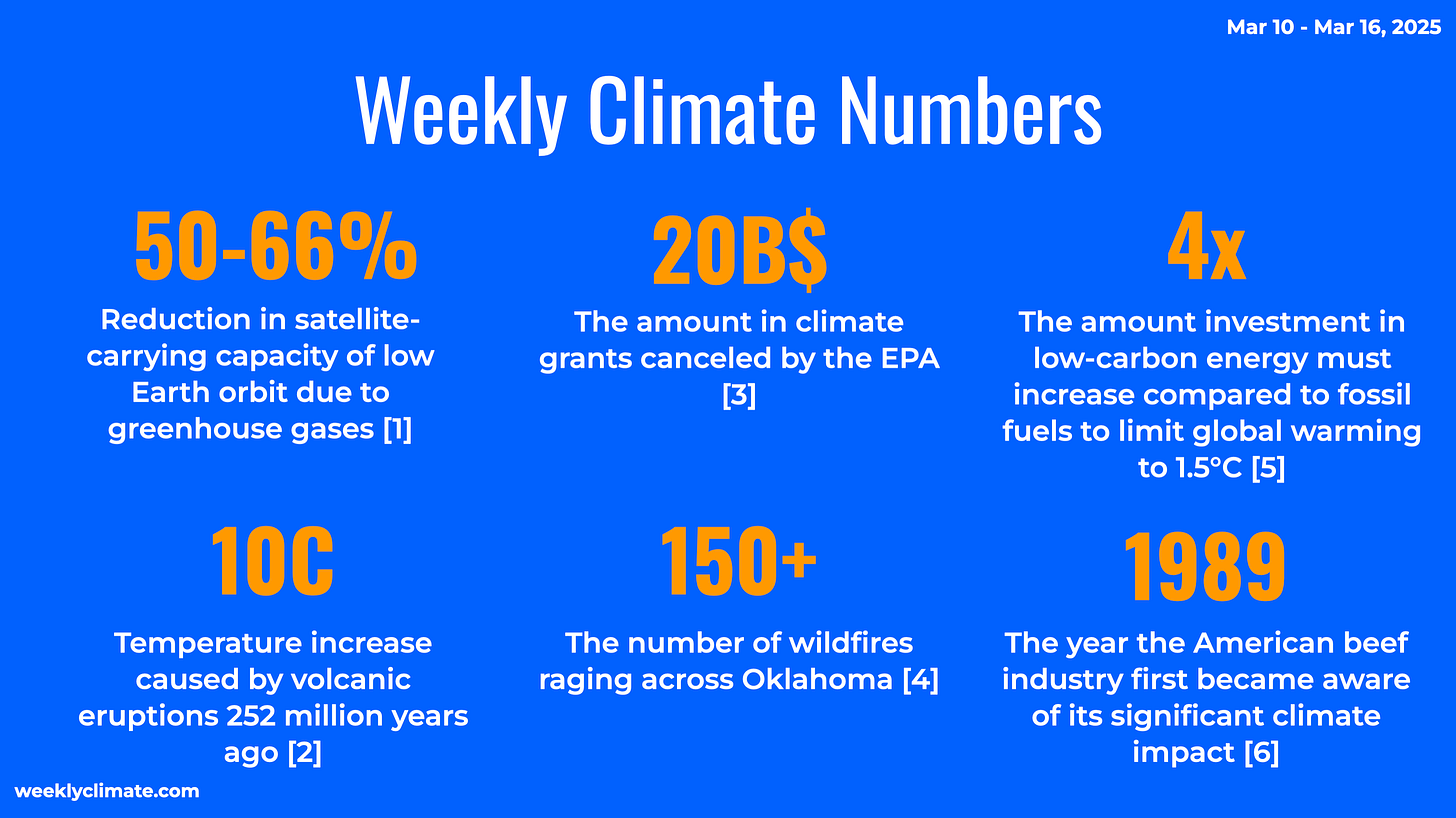
😼 [#Satellite Impacts]: Climate change is surprisingly affecting space infrastructure by shrinking the upper atmosphere, potentially reducing satellite capacity in low Earth orbit by 50-66% by 2100.
💩 [#Fossil Fuel Industry]: Trump's "drill, baby, drill" agenda promotes increased fossil fuel extraction globally while undermining renewable energy efforts, threatening to lock in decades of additional carbon emissions.
👩⚕️ Status: Climate & Science
Let's look at how we're doing this week!
[#Climate History]: Volcanic eruptions 252 million years ago released massive CO2, causing the Great Dying and a significant climate shift, with temperatures rising by 18°F. This study warns that current human CO2 emissions could lead to similar drastic changes in just 2,700 years.
[#Climate Monitoring]: The Mauna Loa Observatory, crucial for tracking greenhouse gases since 1958, faces potential closure due to NOAA budget cuts, which could disrupt vital climate data collection amid significant staff layoffs and proposed lease terminations across the agency.
[#Satellite Impacts]: Climate change is predicted to reduce the satellite-carrying capacity of low Earth orbit by 50-66% by 2100 due to greenhouse gases shrinking the upper atmosphere, increasing collision risks and space debris. Proactive measures are needed to manage satellite launches and mitigate these effects.
📰 The 7 Grand Challenges
⚡️ Decarbonize Electricity
Clean electricity is the one do-or-die challenge we must solve.
[#Renewable Growth] — For the first time in the US, solar and wind energy generated more electricity than coal, with solar being the fastest-growing source. Despite political challenges, demand for electricity is rising, and renewable energy is gaining momentum, indicating a significant shift in the energy landscape.
[#Geothermal Energy] — Geothermal energy is gaining renewed interest as a stable renewable resource, but historical challenges and technical uncertainties persist. Enhanced geothermal systems face economic and operational hurdles, and recent advancements in battery storage are diminishing geothermal's competitive edge.
[#Emerging Markets] — Investment in clean energy technologies like solar, wind, batteries, and hydrogen is crucial for accelerating energy transitions in emerging markets. Targeted interventions can reduce costs, phase out carbon-intensive practices, and support new technology deployment to unlock capital and drive progress.
🏘 Reduce impact of urban and rural areas
Lowering the impact of urban and rural areas.
[#Urban Climate] — Climate change is causing extreme weather patterns in Africa, leading to severe flooding and droughts in cities like Gaborone, Nairobi, and Addis Ababa. Inadequate infrastructure exacerbates the impacts, threatening lives and economies, while urgent investment in stormwater management and climate research is needed to adapt to these challenges.